- Boost Growth: Essential Nutrients
- Macronutrients
- Micronutrients
- Increase Plant Health: Micronutrients
- 1. Iron
- 2. Zinc
- 3. Manganese
- 4. Boron
- 5. Copper
- 6. Molybdenum
- Strengthen Immunity: Plant Hormones
- Auxins
- Cytokinins
- Salicylic Acid
- Enhance Soil Quality: Organic Matter
- 1. Improves Soil Structure:
- 2. Enhances Nutrient Content:
- 3. Increases Water Holding Capacity:
- 4. Stimulates Soil Microorganisms:
- 5. Reduces Soil Compaction:
- 6. Minimizes Soil Erosion:
- Support Photosynthesis: Sunlight
- 1. Importance of Sunlight
- 2. Sunlight Requirements
- 3. Maximizing Sunlight Exposure
- 4. Supplementing Sunlight
- Absorb Nutrients Efficiently: Root System
- Types of Roots
- Root Hairs
- Mycorrhizal Associations
- Roots and Soil Conditions
- Conclusion
- Improve Water Absorption: Moisture Retention
- Protect Against Diseases: Natural Pest Control
- “Question-Answer”
- What are the three simple components in the composition of the vitamin bomb for plants?
- How does the banana peel help plants?
- What benefits do eggshells provide to plants?
- Why are coffee grounds beneficial for plants?
- Can I use the vitamin bomb for all types of plants?
- How often should I use the vitamin bomb on my plants?
- Are there any precautions I should take when using the vitamin bomb?
- “Video” VITAMIN BOMB CUCUMBERS INSTANTLY START RIPPING JUST WATER IT
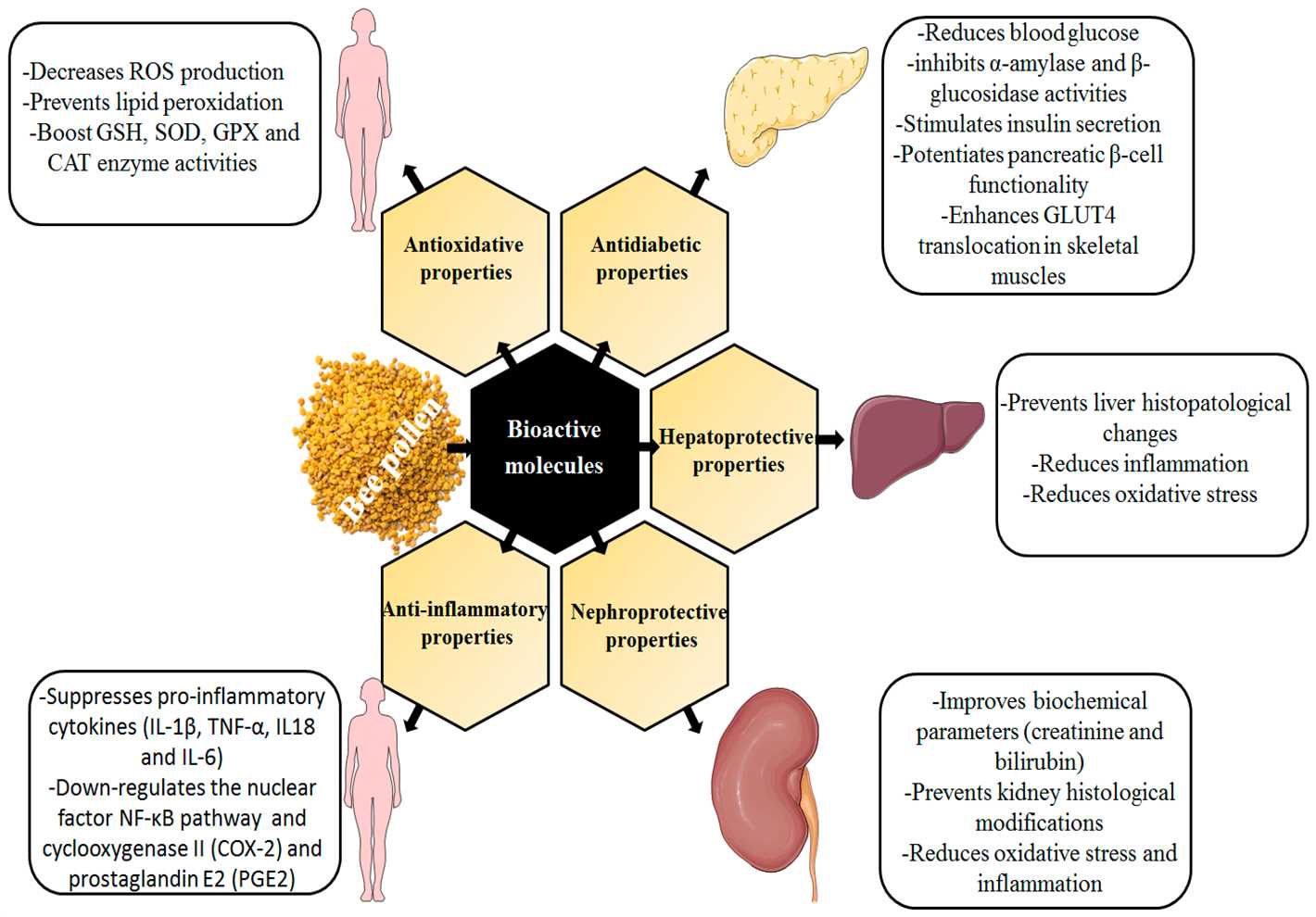
Plants, just like humans, need nutrients to grow and thrive. While they can get some of these nutrients naturally from the soil, sometimes they need a little extra boost. That’s where the “vitamin bomb” comes in. It’s a combination of three simple components that can provide plants with essential nutrients to ensure their health and vitality.
The first component of the vitamin bomb is compost. Compost is a mixture of decomposed organic matter, such as vegetable scraps, leaves, and grass clippings. It acts as a natural fertilizer, enriching the soil with nutrients and improving its structure. When added to plants, compost releases nutrients slowly, providing a long-lasting source of food.
The second component of the vitamin bomb is worm castings. Worm castings are the excrement of earthworms and are rich in nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. They also contain beneficial microorganisms that help fight off plant diseases. Worm castings can be added to the soil or used as a foliar spray to provide plants with a quick nutrient boost.
The third component of the vitamin bomb is seaweed extract. Seaweed is packed with beneficial minerals, vitamins, and plant growth hormones. When used as a fertilizer, seaweed extract improves plant growth, enhances root development, and increases resistance to environmental stressors. It can be applied directly to the soil or used as a foliar spray.
By combining these three simple components, you can create a powerful “vitamin bomb” for your plants. Whether you’re growing flowers, vegetables, or houseplants, giving them this extra boost of nutrients will help them thrive and reach their full potential.
Boost Growth: Essential Nutrients
In order to boost the growth of your plants and ensure their overall health, it is essential to provide them with the necessary nutrients. These nutrients can be divided into two categories: macronutrients and micronutrients.
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are nutrients that are required by plants in relatively large quantities. They play a crucial role in the growth and development of plants. The three primary macronutrients are:
- Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen is essential for the production of proteins and chlorophyll, which are vital for plant growth and photosynthesis.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus plays a key role in energy transfer, root development, and flower formation in plants.
- Potassium (K): Potassium is involved in various physiological processes, including water regulation, enzyme activation, and disease resistance.
These macronutrients are typically found in balanced commercial fertilizers and can also be supplemented through organic materials such as compost and manure.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients, also known as trace elements, are nutrients that are required by plants in smaller quantities. Despite the lower quantity needed, they are equally important for the proper growth and development of plants. Some essential micronutrients for plants include:
- Iron (Fe): Iron is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis and is involved in energy transfer within the plant.
- Zinc (Zn): Zinc plays a crucial role in various enzyme activities and growth hormone regulation.
- Manganese (Mn): Manganese is involved in photosynthesis, nitrogen metabolism, and the breakdown of carbohydrates.
- Boron (B): Boron is essential for cell wall formation, pollen germination, and carbohydrate metabolism.
Micronutrients can be provided to plants through micronutrient fertilizers or through the addition of organic materials such as compost and seaweed extract. It is important to ensure a proper balance of these micronutrients to prevent nutrient deficiencies or toxicities in plants.
By providing plants with the essential macronutrients and micronutrients, you can significantly boost their growth and overall health. Regularly monitoring the nutrient levels and adjusting the fertilization program accordingly is key to ensuring optimum plant growth and development.
Increase Plant Health: Micronutrients
Micronutrients are essential for the optimal growth and health of plants. Although required in small amounts, these nutrients play crucial roles in various physiological and metabolic processes. Here are some important micronutrients that can help boost plant health:
1. Iron
Iron is necessary for the synthesis of chlorophyll and the formation of enzymes involved in energy production. It helps with the transport of electrons during photosynthesis and is essential for the production of new plant cells. Iron deficiency can lead to yellowing leaves and stunted growth.
2. Zinc
Zinc is involved in several enzymatic reactions and plays a vital role in hormone production and regulation. It helps with the synthesis of proteins and DNA, promotes root development, and enhances the overall growth and development of plants. Zinc deficiency can result in reduced crop yields and poor plant health.
3. Manganese
Manganese is essential for photosynthesis as it helps with the breakdown of water molecules, a crucial step in the process. It is also involved in the synthesis of chlorophyll and plays a role in enzyme activation. Manganese deficiency can lead to yellowing of leaves with green veins and reduced plant growth.
4. Boron
Boron is necessary for cell wall formation and stability, pollen germination, and fruit development. It also helps with the uptake and utilization of other nutrients. Boron deficiency can result in hollow stems, distorted growth, and poor fruit and seed production.
5. Copper
Copper is involved in several enzymatic reactions and plays a role in the metabolism of carbohydrates and proteins. It aids in the synthesis of chlorophyll and helps with iron utilization. Copper deficiency can lead to wilting, reduced plant growth, and browning of leaves.
6. Molybdenum
Molybdenum is part of enzymes that convert nitrogen into a form that plants can use for growth. It is crucial for nitrogen fixation and helps with the assimilation of nitrate into amino acids. Molybdenum deficiency can result in yellowing of leaves and reduced plant growth.
Providing plants with a balanced supply of micronutrients is essential for their overall health and productivity. Regular soil testing and the use of fertilizers specifically designed to provide these nutrients can help ensure that plants receive adequate amounts of micronutrients.
Strengthen Immunity: Plant Hormones
Plant hormones play a crucial role in strengthening the immunity of plants. These hormones are chemical messengers that regulate various physiological processes, including growth, development, and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. By understanding the role of plant hormones and incorporating them into the plant’s diet, we can enhance its immune system and overall health.
Auxins
Auxins are a class of plant hormones that promote cell elongation and regulate many aspects of plant growth and development. They play a key role in strengthening the immune system by activating defense pathways in response to pathogens. Auxins also help in the formation of a physical barrier, such as thickening of cell walls, to prevent the entry of pathogens.
Key functions of auxins in strengthening plant immunity:
- Activating defense genes
- Inducing the production of antimicrobial compounds
- Stimulating hypersensitive response to pathogens
Cytokinins

Cytokinins are plant hormones that regulate cell division and differentiation. They play a significant role in boosting plant immunity by enhancing the production of defense-related proteins and metabolites. Cytokinins also help in activating the plant’s systemic acquired resistance (SAR), a broad-spectrum immune response that provides long-lasting protection against various pathogens.
Key functions of cytokinins in strengthening plant immunity:
- Stimulating the production of defense-related proteins
- Activating systemic acquired resistance (SAR)
- Enhancing the synthesis of antimicrobial compounds
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid is a plant hormone that plays a central role in the plant’s defense against pathogens. It acts as a signaling molecule, triggering various defense responses, such as the activation of defense genes and the synthesis of antimicrobial compounds. Salicylic acid is involved in both local and systemic acquired resistance, providing a robust immune response against pathogens.
Key functions of salicylic acid in strengthening plant immunity:
- Activating defense genes
- Inducing the synthesis of antimicrobial compounds
- Promoting the hypersensitive response to pathogens
By providing plants with a balanced diet that includes these essential plant hormones, we can strengthen their immunity and ensure their optimal growth and development. Incorporating natural sources of these hormones, such as plant-based fertilizers and growth promoters, can be an effective way to support the plant’s immune system naturally.
Enhance Soil Quality: Organic Matter
Organic matter plays a crucial role in enhancing soil quality and promoting plant growth. Adding organic matter to the soil can improve its ability to retain moisture, enrich nutrient content, and enhance soil structure. Here are a few ways how organic matter enhances soil quality:
1. Improves Soil Structure:
Organic matter acts as a binding agent for soil particles, improving its structure and stability. It helps in creating pore spaces in the soil, allowing water, air, and roots to penetrate easily. This enhances drainage and reduces the risk of soil erosion.
2. Enhances Nutrient Content:
Organic matter is a rich source of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. When organic matter decomposes, it releases these nutrients back into the soil, making them available for plant uptake. This helps in improving soil fertility and promoting healthy plant growth.
3. Increases Water Holding Capacity:
Adding organic matter to the soil helps in improving its water holding capacity. Organic matter acts as a sponge, absorbing and retaining water, preventing it from leaching away. This ensures that plants have access to a steady supply of moisture, even during dry periods.
4. Stimulates Soil Microorganisms:
Organic matter serves as a food source for beneficial soil microorganisms. These microorganisms play a vital role in decomposing organic matter, releasing nutrients, suppressing plant diseases, and improving soil structure. The presence of organic matter encourages the growth and activity of these microorganisms, promoting a healthy soil ecosystem.
5. Reduces Soil Compaction:
Organic matter helps in reducing soil compaction by improving soil structure and porosity. When soil is compacted, it restricts root growth and limits nutrient and water uptake by plants. Adding organic matter loosens the soil, making it easier for roots to grow and expand, resulting in healthier and more productive plants.
6. Minimizes Soil Erosion:

The organic matter in the soil acts as a protective layer, minimizing the risk of soil erosion. It helps to bind soil particles together, preventing them from being washed away by wind or water. By reducing soil erosion, organic matter helps in preserving the topsoil, which is essential for nutrient cycling and plant growth.
By incorporating organic matter into the soil, gardeners and farmers can significantly improve soil quality, leading to healthier plants and higher crop yields. Composting, using organic mulches, and incorporating cover crops are some effective ways to increase organic matter levels in the soil.
Support Photosynthesis: Sunlight
The process of photosynthesis in plants relies heavily on the presence of sunlight. Sunlight provides the energy necessary for plants to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
1. Importance of Sunlight
Sunlight is crucial for the growth and development of plants. It serves as the primary source of energy for photosynthesis. When sunlight reaches the chlorophyll in plant cells, it initiates a series of biochemical reactions that convert light energy into chemical energy. This energy is then used to fuel the production of glucose and oxygen, which are vital for the plant’s survival.
2. Sunlight Requirements
Plants have varying sunlight requirements depending on their species and growth stage. Some plants, known as full-sun plants, require direct sunlight for most of the day to thrive. These plants usually have thicker leaves and are designed to absorb as much sunlight as possible.
On the other hand, there are shade-tolerant plants that can survive with limited sunlight. These plants have adapted to lower light conditions by having thinner leaves and using alternative means of obtaining energy.
3. Maximizing Sunlight Exposure
To maximize sunlight exposure for your plants:
- Place sun-loving plants in areas of your garden or home where they will receive direct sunlight for at least 6 hours a day.
- Rotate potted plants regularly to ensure all sides receive equal sunlight.
- Trim overhanging branches or nearby foliage that may obstruct sunlight from reaching your plants.
- Consider using reflective surfaces or mirrors strategically positioned to redirect sunlight onto shaded areas.
4. Supplementing Sunlight
In cases where natural sunlight is limited, such as during the winter months or in indoor gardening, artificial light sources can be used to supplement sunlight. Grow lights, specifically designed for plants, emit the required spectrum of light necessary for photosynthesis. These lights can provide plants with the energy they need to grow and thrive even in areas with limited sunlight.
Remember, while sunlight is essential for plants, it’s important to strike a balance. Intense or prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can lead to sunburn and damage the plant. Understanding your plants’ sunlight requirements will help ensure their optimal growth and overall health.
Absorb Nutrients Efficiently: Root System
The root system plays a crucial role in the efficient absorption of nutrients by plants. It serves as the primary interface between the plant and the soil, allowing the plant to take up essential minerals and water.
Types of Roots
There are two main types of roots:
- Taproots: Taproots are primary roots that grow vertically deep into the soil. This type of root system is typically found in dicotyledonous plants, such as carrots, radishes, and dandelions. Taproots provide stability to the plant and allow it to access deep water and nutrients.
- Fibrous roots: Fibrous roots consist of a mass of thin, branching roots that spread out horizontally near the soil surface. This type of root system is common in monocotyledonous plants, including grasses and cereals. Fibrous roots efficiently capture water and nutrients from the topsoil.
Root Hairs
Root hairs are tiny, hair-like projections that emerge from the surface of root cells. They greatly increase the surface area of the root system, enhancing nutrient uptake. The root hairs are responsible for absorbing water and minerals from the soil. These delicate structures are short-lived and continually produced as new cells develop.
Mycorrhizal Associations
Mycorrhizae are beneficial associations between plant roots and fungi. These symbiotic relationships enhance nutrient absorption by the root system. The fungal hyphae extend into the soil, effectively increasing the surface area available for nutrient exchange. In return, the fungi receive organic compounds from the plant.
Roots and Soil Conditions
The health and efficiency of the root system are closely linked to soil conditions. Proper aeration, soil moisture, and pH levels are crucial for optimal root development and function. Compacted or waterlogged soil can restrict root growth and hinder nutrient absorption. It is important to maintain a well-draining soil environment to support the health of the plant’s root system.
Conclusion
The root system is a vital component of a plant’s ability to absorb nutrients efficiently. Whether it is a taproot or fibrous root system, the roots play a crucial role in anchoring the plant, absorbing water and minerals, and forming beneficial associations with fungi. Maintaining healthy soil conditions is essential for supporting optimal root development and ensuring the overall health and growth of the plant.
Improve Water Absorption: Moisture Retention
Moisture retention is an essential factor in improving water absorption for plants. It helps to prevent the evaporation of water from the soil and ensures that the plants can absorb the necessary moisture for their growth and development.
There are several ways to improve moisture retention in the soil:
- Use organic matter: Adding organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to the soil helps to improve its moisture-holding capacity. Organic matter acts like a sponge, absorbing and retaining water in the soil for a longer period of time.
- Mulching: Applying a layer of mulch on the soil surface helps to create a barrier that reduces evaporation and retains moisture. Organic mulches like straw, bark, or wood chips work well in retaining moisture and also provide additional benefits such as weed control and temperature regulation.
- Watering techniques: The way you water your plants can also affect moisture retention. Instead of frequent shallow watering, it is better to water deeply and less often. This promotes deep root growth and ensures that the water reaches the lower layers of the soil, where it can be retained for a longer time.
In addition to these methods, it is important to choose the right plants for your garden that are adapted to your climate and soil conditions. Some plants are naturally more resistant to drought and have mechanisms to conserve water, which can help in improving moisture retention.
By implementing these moisture retention techniques, you can ensure that your plants have a constant and adequate water supply, leading to healthier and more productive growth.
Protect Against Diseases: Natural Pest Control
Natural pest control is a vital aspect of plant care to protect against diseases and ensure healthy growth. Chemical pesticides can harm the environment and even human health, so it’s important to explore natural alternatives. Here are some effective methods for natural pest control:
- Encourage beneficial insects: Certain insects, like ladybugs and lacewings, feed on harmful pests such as aphids and mites. To attract these beneficial insects, plant flowers like marigolds, cosmos, and daisies in your garden.
- Use neem oil: Neem oil is a natural pesticide derived from the neem tree. It is effective against a wide range of pests and can be used on various plants. Dilute neem oil in water and spray it on the affected plants to control pests.
- Introduce predatory insects: Predatory insects like praying mantis and predatory nematodes can be beneficial for controlling pests. You can release them in your garden to naturally keep pest populations in check.
- Practice crop rotation: Crop rotation involves changing the location of crops each year to disrupt pest life cycles. This can help prevent the buildup of pests in the soil and reduce the risk of disease.
- Utilize companion planting: Certain plants can repel pests or attract beneficial insects when planted together. For example, planting basil near tomatoes can deter aphids.
- Remove infected plants: If a plant is severely infected with pests or diseases, it’s best to remove it from the garden to prevent the spread of the problem to other plants.
By practicing natural pest control methods, you can protect your plants from diseases and maintain a healthy garden ecosystem.
“Question-Answer”
What are the three simple components in the composition of the vitamin bomb for plants?
The three simple components in the composition of the vitamin bomb for plants are banana peel, eggshell, and coffee grounds.
How does the banana peel help plants?
Banana peel is rich in potassium, which is essential for plant growth. It also contains other nutrients like phosphorus and calcium, which can promote root development and overall plant health.
What benefits do eggshells provide to plants?
Eggshells are a great source of calcium for plants. They also help to deter pests like slugs and snails, as the sharp edges of the crushed eggshells can be uncomfortable for these pests to crawl over.
Why are coffee grounds beneficial for plants?
Coffee grounds contain nitrogen, which is an important nutrient for plant growth. They also improve soil drainage and can attract earthworms, which help to aerate the soil.
Can I use the vitamin bomb for all types of plants?
Yes, the vitamin bomb can be used for a wide variety of plants including vegetables, herbs, flowers, and houseplants. However, it is important to use the mixture in moderation and adjust the quantities based on the specific needs of your plants.
How often should I use the vitamin bomb on my plants?
The frequency of using the vitamin bomb on your plants will depend on several factors such as the type of plants, their growth stage, and the condition of the soil. As a general guideline, you can apply the mixture once every 2-4 weeks during the growing season.
Are there any precautions I should take when using the vitamin bomb?
When using the vitamin bomb, it is important to avoid over-fertilizing your plants as this can cause nutrient burn. Start with small amounts of the mixture and observe how your plants respond before increasing the dosage. Additionally, ensure that the banana peels, eggshells, and coffee grounds are properly decomposed before using them on your plants to prevent attracting pests.







