- Importance of Water Heating in the Greenhouse
- 1. Plant Growth and Development
- 2. Frost Protection
- 3. Soil Conditioning
- 4. Season Extension
- 5. Energy Efficiency
- Benefits of Heating Both Air and Soil
- 1. Enhanced Root Development
- 2. Improved Plant Growth
- 3. Extended Growing Season
- 4. Energy Efficiency
- 5. Disease Prevention
- 6. Increased Crop Yield
- Different Methods of Water Heating in the Greenhouse
- 1. Boiler System
- 2. Solar Water Heating
- 3. Geothermal Heating
- 4. Waste Heat Recovery
- Choosing the Right Heating System for Your Greenhouse
- 1. Type of Fuel:
- 2. Heating Capacity:
- 3. Distribution Method:
- 4. Energy Efficiency:
- 5. Budget:
- 6. Maintenance and Durability:
- 7. Climate Considerations:
- 8. Safety Measures:
- Tips for Efficient Water Heating
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- “Question-Answer”
- What are the benefits of heating both air and soil in a greenhouse?
- What are some common methods of heating the air in a greenhouse?
- How can soil be heated in a greenhouse?
- Are there any energy-efficient options for heating a greenhouse?
- How can I determine the heating requirements for my greenhouse?
- What are some tips for more efficient water heating in a greenhouse?
- “Video” This NEW GREENHOUSE has "NEW BUSINESS" written ALL over it!
Heating is a crucial aspect of maintaining optimal conditions in a greenhouse. As temperatures drop outside, it becomes necessary to provide a source of warmth to keep plants healthy and thriving. While there are various methods of greenhouse heating available, one effective approach is water heating. By using water as a heat source, both the air and soil in the greenhouse can be heated simultaneously, creating an ideal environment for plants to grow.
Water heating works by circulating hot water through pipes or tubes in the greenhouse. The warmed water releases heat into the surrounding air, raising its temperature and providing warmth to the plants. Some systems also include underground pipes or tubes that heat the soil directly. This dual heating method ensures that both the air and soil temperatures are regulated, promoting optimal growing conditions.
One advantage of water heating in a greenhouse is its energy efficiency. Water has a high thermal mass, meaning it can store and release heat over an extended period. This allows the greenhouse to retain heat even when the heating system is turned off temporarily. Additionally, water heating systems can be powered by renewable energy sources such as solar collectors, making them an environmentally-friendly option.
There are different types of water heating systems available for use in greenhouses. One common method is the use of boilers or hot water heaters to heat the water before circulating it through the greenhouse. Another option is to use geothermal heat pumps that extract heat from the ground and transfer it to the water. These systems can be tailored to suit the specific needs of the greenhouse and its plants.
Importance of Water Heating in the Greenhouse
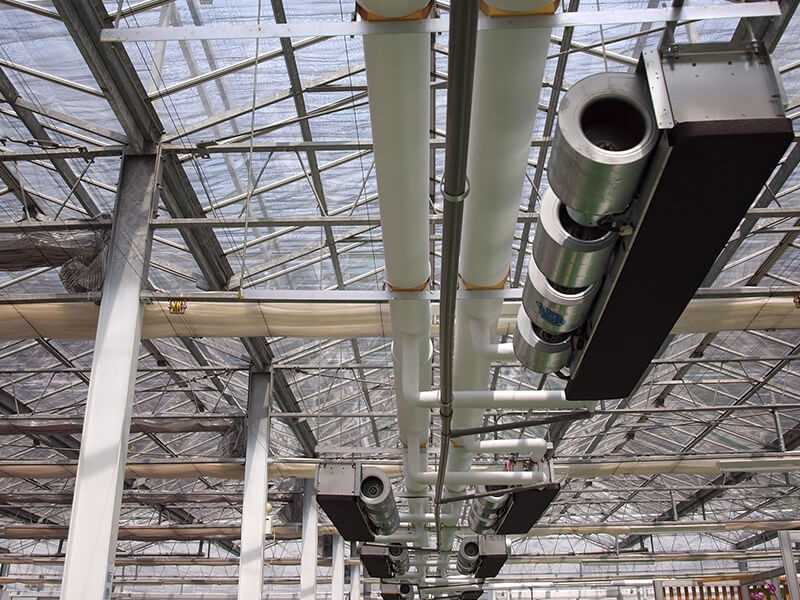

Water heating plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal conditions for plant growth in a greenhouse. By providing warmth to both the air and soil, it creates a favorable environment for plants to thrive throughout the year, regardless of external weather conditions.
1. Plant Growth and Development
Water heating in the greenhouse is essential for promoting plant growth and development. Plants require specific temperature ranges to carry out essential physiological processes effectively. Heating the water helps regulate the temperature inside the greenhouse, ensuring that it stays within the ideal range for optimal plant growth. This is especially important during colder months when low temperatures can slow down plant growth and negatively affect yield.
2. Frost Protection
During cold winter nights, frost can be detrimental to plants in the greenhouse. By circulating warm water through the system, water heating provides protection against frost damage. The heated water warms the air inside the greenhouse, preventing the temperature from falling too low and safeguarding plants from frost. This is particularly crucial for sensitive plants that are prone to frost damage.
3. Soil Conditioning
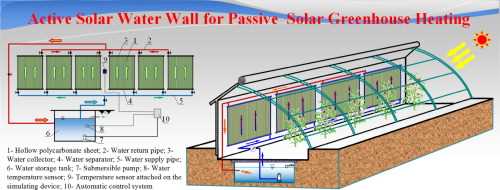
Water heating also plays a vital role in soil conditioning. When the water is heated, it warms up the soil as well. This helps maintain optimal soil temperature, which is essential for root development and nutrient absorption by plants. A warm soil temperature encourages robust root growth, leading to healthier and more productive plants.
4. Season Extension
Heating water in the greenhouse allows for season extension, meaning that plants can be grown outside their normal growing season. By creating a warm and stable environment, water heating enables growers to start planting earlier in the spring and continue harvesting later in the fall. This extension of the growing season can significantly increase crop yields and provide farmers with a longer window for plant cultivation and sales.
5. Energy Efficiency
Water heating systems in greenhouses can be designed to be energy-efficient. By using energy sources like solar panels or heat pumps, the greenhouse can reduce its reliance on non-renewable energy sources. This not only lowers operational costs but also contributes to sustainability efforts in agriculture. Energy-efficient water heating systems can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and minimize the environmental footprint of greenhouse operations.
In conclusion, water heating is of great importance in greenhouse cultivation. It creates optimal conditions for plant growth, provides frost protection, conditions the soil, extends the growing season, and promotes energy efficiency. Implementing a reliable water heating system is key to ensuring successful plant cultivation in greenhouses.
Benefits of Heating Both Air and Soil
Heating both the air and soil in a greenhouse offers several benefits for plant growth and productivity. By providing optimal conditions for both the roots and the foliage, this dual approach to heating can result in healthier plants, higher yields, and better overall greenhouse performance.
1. Enhanced Root Development
When both the air and soil are heated, plants benefit from a more stable and uniform temperature throughout the greenhouse. This helps promote healthy root development, as the roots are exposed to consistent warmth, which encourages their growth. Well-developed roots are essential for nutrient uptake and water absorption, leading to stronger and more productive plants.
2. Improved Plant Growth
Heating both the air and soil creates optimal growing conditions for plants. Warm air promotes photosynthesis and allows plants to produce energy for growth. At the same time, warm soil provides the necessary nutrients and moisture to support plant growth. By combining these two elements, plants are able to thrive and reach their full potential.
3. Extended Growing Season
Heating both the air and soil in a greenhouse extends the growing season, allowing for year-round cultivation. By maintaining the right temperature, even during colder months, plants can continue to grow and produce crops. This is especially beneficial for greenhouse operators who rely on consistent harvests and need to maximize their productivity.
4. Energy Efficiency

While heating both the air and soil may initially require more energy, it can actually lead to increased energy efficiency in the long run. By creating a balanced and controlled environment, there is less energy wasted on compensating for temperature fluctuations. Additionally, heating the soil helps retain heat overnight, reducing the need for additional heating during the night.
5. Disease Prevention
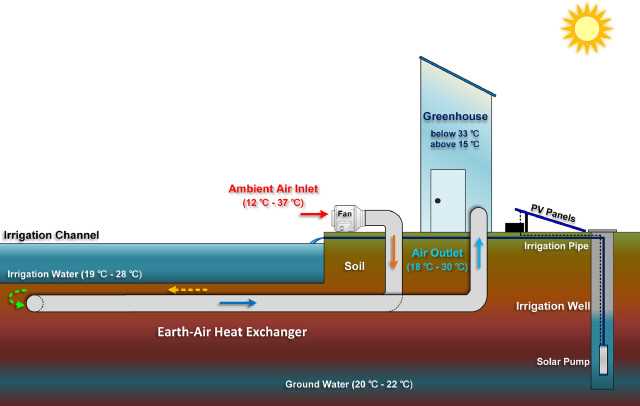
By heating both the air and soil, the overall greenhouse environment becomes less favorable for the growth of pathogens and disease-causing organisms. The stable and warm conditions discourage the development and spread of diseases, protecting the plants from potential harm. This can help reduce the need for chemical treatments and result in healthier plants.
6. Increased Crop Yield
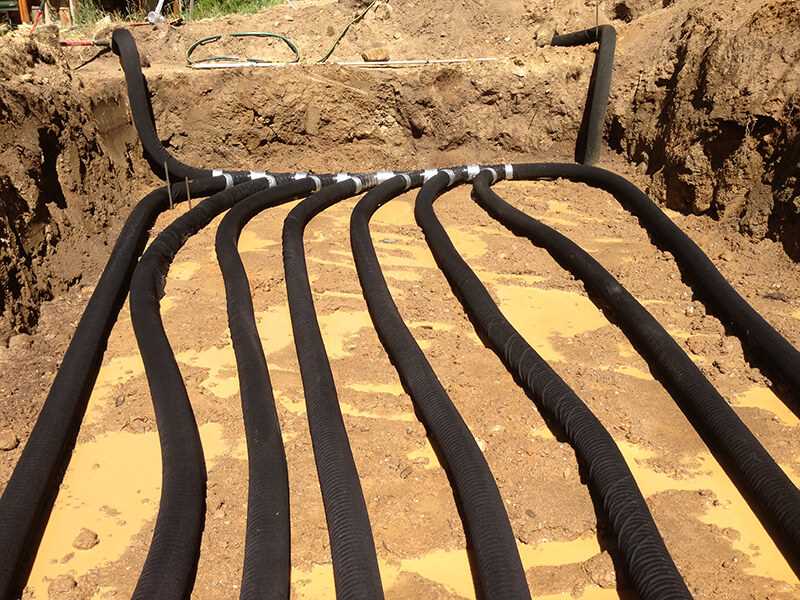

Ultimately, heating both the air and soil in a greenhouse can lead to increased crop yield. The combination of optimal growing conditions, extended growing season, and disease prevention results in healthier, stronger plants that are able to produce more fruits or vegetables. This can have a significant impact on the profitability and success of a greenhouse operation.
Overall, heating both the air and soil in a greenhouse offers numerous benefits for plant growth and productivity. By creating favorable conditions for roots and foliage, greenhouse operators can optimize their growing environment and achieve better results.
Different Methods of Water Heating in the Greenhouse
Heating water is an essential element in maintaining an optimal growing environment in the greenhouse. There are several different methods that can be used to heat water in the greenhouse, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
1. Boiler System
A boiler system is a traditional method of water heating in the greenhouse. It involves the use of a boiler, which heats the water and distributes it through pipes to radiators or heat exchangers placed throughout the greenhouse. The boiler can be fueled by various sources such as natural gas, propane, or oil.
- Advantages: Boiler systems provide reliable and consistent heat distribution, making them suitable for larger greenhouse operations. They can also be used for heating both the air and the soil.
- Disadvantages: Boiler systems can be expensive to install and maintain. They also require a constant supply of fuel and can pose a risk of carbon monoxide emissions if not properly maintained.
2. Solar Water Heating
Solar water heating is an eco-friendly method that utilizes the energy from the sun to heat the water. It involves the installation of solar panels, which capture sunlight and convert it into heat. This heat is then transferred to the water through a series of pipes and a heat exchanger.
- Advantages: Solar water heating is a sustainable and cost-effective method that can significantly reduce energy consumption. It is especially beneficial in areas with ample sunlight.
- Disadvantages: Solar water heating is highly dependent on sunlight availability and may not provide sufficient heat during cloudy or winter months. It may also require a backup heating system in case of insufficient solar energy.
3. Geothermal Heating

Geothermal heating utilizes the natural heat from the ground to warm the water. It involves the installation of a system of pipes buried underground, where the water is circulated and heated by the Earth’s heat.
- Advantages: Geothermal heating is a sustainable and energy-efficient method that provides consistent heat throughout the year. It can significantly reduce energy costs and has a minimal carbon footprint.
- Disadvantages: Geothermal heating requires significant upfront investment and may not be feasible in all locations, particularly in areas with limited access to geothermal resources.
4. Waste Heat Recovery
Waste heat recovery involves capturing and utilizing the excess heat produced by other greenhouse systems or processes. This heat is then transferred to the water, providing an additional source of heating.
- Advantages: Waste heat recovery is a cost-effective method that utilizes existing energy sources, reducing the need for additional heating systems.
- Disadvantages: The availability of waste heat depends on the specific greenhouse systems and processes in place. It may not provide sufficient heat for all greenhouse heating needs.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Boiler System | Reliable and consistent heat distribution, suitable for larger greenhouse operations | Expensive to install and maintain, requires a constant supply of fuel |
| Solar Water Heating | Sustainable and cost-effective, reduces energy consumption | Dependent on sunlight availability, may require a backup heating system |
| Geothermal Heating | Sustainable and energy-efficient, provides consistent heat throughout the year | Requires significant upfront investment, may not be feasible in all locations |
| Waste Heat Recovery | Cost-effective, utilizes existing energy sources | Dependent on the availability of waste heat, may not provide sufficient heat for all needs |
Choosing the Right Heating System for Your Greenhouse
When it comes to heating your greenhouse and providing the ideal temperature for your plants, it’s essential to choose the right heating system. The right system will not only keep your greenhouse warm but also ensure energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a heating system for your greenhouse:
1. Type of Fuel:
Choosing the right type of fuel for your heating system is crucial. You can opt for natural gas, propane, electricity, or even biomass. Consider the availability and cost of fuel in your area, as well as the environmental impact of the fuel source.
2. Heating Capacity:
Determine the heating capacity you need for your greenhouse. This will depend on the size of your greenhouse, the desired temperature, and the plants you are growing. Consult with a professional to calculate the required heating capacity accurately.
3. Distribution Method:
Consider how the heat will be distributed throughout your greenhouse. Common distribution methods include forced-air systems, radiant heating, and under-bench heating. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, so choose the one that suits your specific needs and budget.
4. Energy Efficiency:
Energy efficiency is an important aspect to consider to minimize greenhouse heating costs. Look for heating systems with high energy efficiency ratings or those that incorporate energy-saving features such as programmable thermostats and zoning capabilities.
5. Budget:
Set a budget for your greenhouse heating system and stick to it. Consider not only the initial installation costs but also the long-term operating costs. Remember that investing in a high-quality, energy-efficient system may save you money in the long run.
6. Maintenance and Durability:

Consider the maintenance requirements and durability of the heating system. Look for systems that are easy to maintain and have a long lifespan. Regular maintenance will ensure optimal performance and extend the life of your heating system.
7. Climate Considerations:
Take into account your specific climate and weather conditions. Some heating systems may be more suitable for colder climates, while others may perform better in moderate climates. Consider factors such as insulation, ventilation, and the presence of additional heating sources.
8. Safety Measures:
Ensure that your chosen heating system incorporates safety features to protect both your greenhouse and the plants. Features such as automatic shut-off valves, temperature controls, and overheating protection are essential to prevent accidents and damage.
By considering these factors and consulting with professionals, you can choose the right heating system for your greenhouse that meets your specific requirements and helps create the ideal growing environment for your plants.
Tips for Efficient Water Heating
Proper water heating in a greenhouse can greatly contribute to creating and maintaining optimal growing conditions for plants. Here are some tips for efficient water heating:
- Use an insulated water storage tank: Insulating the water storage tank helps to reduce heat loss and maintain the temperature of the water for longer periods.
- Consider using a solar water heater: Solar water heaters can utilize the energy from the sun to heat the water, reducing energy costs and making the system more environmentally friendly.
- Install a heat exchanger: Using a heat exchanger can improve energy efficiency by transferring heat from hot waste water to the incoming cold water, reducing the energy required to heat the water.
- Use a high-efficiency boiler or water heater: Investing in a high-efficiency boiler or water heater can help to reduce energy consumption and lower heating costs in the long run.
- Insulate water pipes: Insulating the water pipes can help to prevent heat loss and maintain water temperature as it travels from the heater to the greenhouse.
- Utilize efficient water circulation: Implementing a well-designed water circulation system ensures that hot water reaches all areas of the greenhouse efficiently, reducing energy waste and promoting uniform heating.
- Implement temperature controls: Installing temperature controls in the water heating system allows for precise temperature management, ensuring that the water is heated only when necessary and preventing overheating.
- Maintain regular maintenance: Regular maintenance of the water heating system, including checking for leaks, cleaning filters, and ensuring proper functioning of components, can help to optimize performance and prevent energy waste.
By following these tips, greenhouse owners can improve the efficiency of their water heating system, reduce energy consumption, and create optimal growing conditions for their plants.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting

Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the efficient and effective operation of the water heating system in your greenhouse. Regular maintenance tasks include:
- Inspecting the water heating equipment for leaks or damage.
- Cleaning the water heating system to remove any debris or sediment that may have accumulated.
- Checking and adjusting the temperature settings on the water heater to ensure optimal performance.
- Inspecting and cleaning the air and soil heating elements to ensure they are functioning properly.
- Checking and replacing any worn or damaged components, such as pipes or valves.
In addition to regular maintenance, it is important to be familiar with common troubleshooting techniques to address any issues that may arise. Some common troubleshooting steps include:
- Checking the water supply to ensure there is an adequate flow of water.
- Checking for any air or water leaks in the system and repairing them if necessary.
- Verifying that the thermostat is set correctly and adjusting it if needed.
- Inspecting the electrical connections and ensuring they are secure.
- Testing the control panel and sensors to ensure they are functioning properly.
If you encounter any issues that you are unable to resolve on your own, it is recommended to seek professional assistance. A qualified technician can diagnose and repair more complex issues with your water heating system.
By following a regular maintenance schedule and addressing any issues promptly, you can keep your water heating system in good working order and ensure optimal heating for both the air and soil in your greenhouse.
“Question-Answer”
What are the benefits of heating both air and soil in a greenhouse?
Heating both the air and soil in a greenhouse has several benefits. Firstly, it helps to maintain a stable and optimal growing environment for plants, ensuring they have the right temperature for growth. Secondly, it can help to increase the yield and production of crops, as warm soil stimulates root growth and nutrient uptake. Lastly, heating both the air and soil can help to extend the growing season, allowing for year-round cultivation in colder climates.
What are some common methods of heating the air in a greenhouse?
There are several common methods of heating the air in a greenhouse. One option is to use a forced-air system, which involves using fans or blowers to circulate warm air throughout the greenhouse. Another option is to use radiant heating, which involves installing heating pipes or panels that emit heat directly into the air. Other methods include using electric heaters, propane or natural gas heaters, or even wood-burning stoves.
How can soil be heated in a greenhouse?
There are a few different methods for heating the soil in a greenhouse. One option is to use geothermal heat, which involves harnessing the natural heat from the earth by installing underground pipes filled with a heat-transfer fluid. Another option is to use electric heating cables or mats that are placed directly in the soil. Another method is to use radiant heating panels or pipes that are installed in the greenhouse floor and emit heat upwards into the soil.
Are there any energy-efficient options for heating a greenhouse?
Yes, there are several energy-efficient options for heating a greenhouse. One option is to use solar panels to capture and convert sunlight into electricity, which can then be used to power electric heaters or heating systems. Another option is to use a heat pump, which can extract heat from the air or ground and transfer it into the greenhouse. Additionally, using proper insulation, sealing any air leaks, and using energy-efficient heating systems can also help to reduce energy consumption.
How can I determine the heating requirements for my greenhouse?
There are a few factors to consider when determining the heating requirements for a greenhouse. These include the size and volume of the greenhouse, the desired temperature range, the local climate and outdoor temperatures, the insulation and heat retention capabilities of the greenhouse structure, and the heat loss through air leaks. It can be helpful to consult with a greenhouse heating specialist or use online calculators to get a more accurate estimate of the heating requirements.
What are some tips for more efficient water heating in a greenhouse?
There are several tips for more efficient water heating in a greenhouse. Firstly, it’s important to insulate the water storage tanks or pipes to minimize heat loss. This can be done using insulation materials such as foam or pipe insulation. Secondly, using a water circulation system can help to distribute the heat more evenly throughout the greenhouse. Additionally, using a timer or thermostat to control when the water heating system operates can help to minimize energy consumption.







