- Properties of Wood Ash
- 1. Composition
- 2. Alkalinity
- 3. Nutrient Content
- 4. Slow-release Fertilizer
- 5. Soil Amendments
- 6. Pest and Disease Control
- 7. Environmental Considerations
- Benefits of Using Wood Ash as a Fertilizer
- 1. Supplying Nutrients
- 2. Balancing Soil pH
- 3. Enhancing Soil Structure
- 4. Deterring Pests
- 5. Preventing Certain Plant Diseases
- 6. Promoting Fruit Set
- 7. Cost-Effective Option
- 8. Environmentally Friendly
- Benefits of Using Wood Ash as a Disease Remedy
- How to Use Wood Ash as a Fertilizer
- How to Use Wood Ash as a Disease Remedy
- 1. Prepare the wood ash
- 2. Test the pH level
- 3. Apply the wood ash
- 4. Monitor the plants
- 5. Use it in combination with other remedies
- Precautions and Risks of Using Wood Ash
- Contamination
- pH Imbalance
- Salt Buildup
- Nutrient Imbalance
- Environmental Impact
- “Question-Answer”
- What is wood ash?
- What are the benefits of using wood ash as a fertilizer?
- How can wood ash be used to control diseases in plants?
- Is wood ash suitable for all types of plants?
- How should wood ash be applied as a fertilizer?
- Can wood ash be harmful to plants if used incorrectly?
- Are there any safety precautions to keep in mind when using wood ash?
- “Video” How to use fresh chicken manure in your garden and chicken update
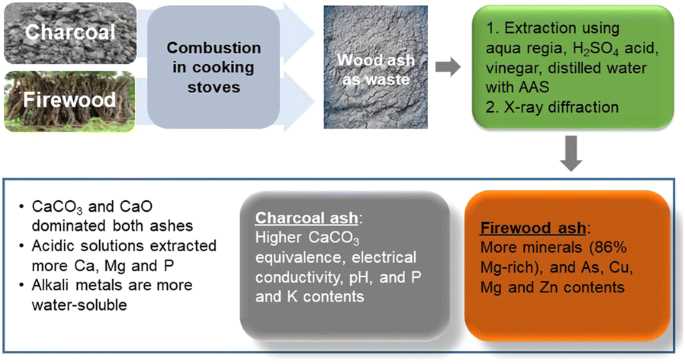
Wood ash is a valuable byproduct of burning wood and has been used for centuries for its various benefits and properties. It is composed primarily of calcium carbonate, potassium carbonate, and other trace elements. Wood ash is alkaline in nature and can be used to adjust the pH levels of soil, making it more suitable for certain plants and crops.
One of the main benefits of wood ash as a fertilizer is its high potassium content. Potassium is an essential nutrient for plants, aiding in their overall growth and development. By adding wood ash to the soil, plants can benefit from the increased potassium levels, resulting in healthier and more robust growth.
In addition to its fertilizer properties, wood ash has also been used as a disease remedy for plants. The alkaline nature of wood ash can help to suppress certain fungal and bacterial diseases, such as powdery mildew and blight. It acts as a natural fungicide and can be applied as a preventative measure or as a treatment for existing plant diseases.
Wood ash is a versatile substance that can be used in various ways. It can be applied directly to the soil as a fertilizer, either by sprinkling it on the surface or by incorporating it into the soil during planting. Wood ash can also be used to create a liquid fertilizer by steeping it in water and then using the solution to water plants. Additionally, wood ash can be mixed with water to create a paste and applied directly to the leaves of plants affected by fungal diseases.
It is important to note that wood ash should be used in moderation and with caution. Excessive use of wood ash can raise the pH levels of the soil too much, causing harm to plants that prefer acidic conditions. It is recommended to perform a soil test before using wood ash as a fertilizer and to follow specific guidelines for application rates based on the type of plants being grown.
In conclusion, wood ash is a valuable resource that can be used as a fertilizer and disease remedy for plants. Its high potassium content and alkaline nature make it beneficial for plant growth, while its fungicidal properties help to combat diseases. However, it is important to use wood ash in moderation and with care to avoid disrupting the pH balance of the soil. With proper usage, wood ash can be a sustainable and effective way to improve plant health and productivity.
Properties of Wood Ash
1. Composition
Wood ash is primarily composed of calcium carbonate, also known as lime, which makes up a significant portion of its overall composition. Other important elements found in lesser amounts include potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium.
2. Alkalinity
Due to its high calcium carbonate content, wood ash has alkaline properties. This means that it has the ability to neutralize acidic soils, raising the pH levels to more alkaline levels. This can be beneficial for plants that prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil conditions.
3. Nutrient Content
Wood ash is a good source of important nutrients, such as potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium. These nutrients are essential for plant growth and development. However, it is important to note that the nutrient content may vary depending on the type of wood burned.
4. Slow-release Fertilizer

When used as a fertilizer, wood ash acts as a slow-release source of nutrients. It releases these nutrients gradually over time, providing a continuous supply for plant uptake. This slow-release property can help prevent nutrient leaching and reduce the risk of over-fertilization.
5. Soil Amendments
Wood ash can be used as a soil amendment to improve soil structure and fertility. It can help improve water and nutrient retention in sandy soils and enhance drainage in clay soils. Additionally, it can increase the cation exchange capacity of the soil, improving its ability to hold and exchange essential nutrients.
6. Pest and Disease Control
Wood ash has been used traditionally as a natural remedy for pest and disease control. It can help deter certain garden pests, such as slugs and snails, due to its abrasive texture. It has also been found to suppress certain fungal diseases, such as powdery mildew, when applied to affected plants.
7. Environmental Considerations

Wood ash is a byproduct of burning wood, which is a renewable resource. When using wood ash as a fertilizer, it is important to consider the source of the wood to ensure it is from sustainable and responsibly managed forests. Additionally, excessive use of wood ash can contribute to soil alkalinity, which may not be suitable for all plant species.
Benefits of Using Wood Ash as a Fertilizer
Wood ash is a valuable source of nutrients for plants and can be used as a fertilizer in many gardening applications. Its benefits as a fertilizer include:
1. Supplying Nutrients

Wood ash is rich in essential plant nutrients, such as potassium, phosphorus, and calcium. These nutrients are vital for the growth and development of plants.
2. Balancing Soil pH
Wood ash is alkaline in nature and can be used to balance soil pH levels. It can help neutralize acidic soils, creating a more favorable environment for plant growth.
3. Enhancing Soil Structure
Wood ash contains fine particles that can improve the structure of clay soils, making them easier to work with. It can also increase water drainage in heavy soils, preventing waterlogging and improving aeration.
4. Deterring Pests
Several pests, such as slugs and snails, dislike alkaline environments. By applying wood ash around the base of plants, you can create a barrier that deters these pests.
5. Preventing Certain Plant Diseases
Wood ash contains potassium, which plays a role in disease resistance in plants. By providing plants with sufficient potassium, wood ash can help prevent diseases caused by nutrient deficiencies.
6. Promoting Fruit Set
Wood ash is particularly beneficial for fruit trees and bushes. Its high potassium content promotes flower and fruit formation, resulting in increased yield and improved fruit quality.
7. Cost-Effective Option
Using wood ash as a fertilizer is a cost-effective alternative to commercial fertilizers. It is a natural byproduct that can be easily obtained from the burning of wood, making it an environmentally-friendly choice.
8. Environmentally Friendly
Wood ash is a sustainable and eco-friendly fertilizer option. It is a recycled waste product and reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers, which can have harmful effects on the environment.
Overall, utilizing wood ash as a fertilizer can provide numerous benefits for your plants, soil, and the environment. However, it is essential to use it in moderation and determine its suitability for specific plants and soil conditions.
Benefits of Using Wood Ash as a Disease Remedy
- Organic Solution: Wood ash is a natural and organic remedy for various diseases that affect plants. Unlike chemical pesticides, wood ash does not contain harmful synthetic substances that may have negative effects on plants or the environment.
- Antifungal Properties: Wood ash contains compounds such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium that have antifungal properties. These properties make wood ash an effective remedy for fungal diseases that commonly affect plants, such as powdery mildew and black spot.
- Reduces Disease Spread: Applying wood ash to plants helps to reduce the spread of diseases. The alkaline nature of wood ash creates an unfavorable environment for disease-causing organisms, preventing them from thriving and spreading.
- Boosts Plant Immunity: Wood ash contains essential nutrients that can strengthen plant immune systems. The nutrients help plants develop stronger cell walls and better resistance to pathogens, reducing their susceptibility to diseases.
- Improves Soil pH: Wood ash can be used to amend acidic soils, raising their pH levels. This is beneficial for plants as it creates an environment where disease-causing organisms struggle to survive.
- Cost-Effective: Using wood ash as a disease remedy is cost-effective as it is a byproduct of burning wood, which is widely available and often free or inexpensive to obtain. This makes it an affordable option for gardeners and farmers.
Overall, wood ash offers several benefits as a disease remedy for plants. Its organic nature, antifungal properties, ability to reduce disease spread, boost plant immunity, improve soil pH, and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice among gardeners and farmers seeking natural solutions for plant diseases.
How to Use Wood Ash as a Fertilizer
Wood ash is a valuable source of nutrients that can be used as a fertilizer in your garden. Here are some tips on how to use wood ash effectively:
- Test the pH: Before using wood ash, it’s important to test the pH level of your soil. Wood ash is alkaline, so it should only be used in soils that are too acidic (pH below 7). Avoid using wood ash in soils that are already alkaline or neutral.
- Apply in moderation: Wood ash should be used in moderation, as excessive use can lead to nutrient imbalances in the soil. Start by applying a thin layer of wood ash on the soil surface, and then work it into the soil using a rake or a hoe. Repeat the application once or twice a year, depending on the needs of your plants.
- Avoid direct contact with plant roots: When applying wood ash, make sure to avoid direct contact with the roots of plants. Too much wood ash in the immediate vicinity of plant roots can be harmful to their growth.
- Use in compost: Wood ash can also be added to your compost pile. Mix it with other organic matter such as leaves, grass clippings, and vegetable scraps to create nutrient-rich compost for your plants.
- Use as a soil amendment: Wood ash can be used as a soil amendment to improve the structure and fertility of the soil. It helps to loosen clay soils and increase the water-holding capacity of sandy soils.
- Avoid using on acid-loving plants: Wood ash is not suitable for acid-loving plants such as azaleas, rhododendrons, and blueberries. These plants prefer acidic soils, and the alkaline nature of wood ash can harm their growth.
- Mix with other fertilizers: To maximize the benefits of wood ash, you can mix it with other organic fertilizers such as compost, manure, or bone meal. This will provide a balanced nutrient supply to your plants.
In summary, wood ash can be a valuable addition to your garden as a fertilizer. However, it should be used with caution and in moderation. Test the pH of your soil, avoid direct contact with plant roots, and consider mixing it with other fertilizers or using it in compost. By following these guidelines, you can reap the benefits of wood ash and improve the health and productivity of your plants.
How to Use Wood Ash as a Disease Remedy
Wood ash can be an effective natural remedy for controlling and preventing diseases in plants. Here are some tips on how to use wood ash as a disease remedy:
1. Prepare the wood ash
Collecting: Start by collecting wood ash from burning hardwood. Avoid using ashes from treated wood or materials that may contain chemicals.
Storing: Store the wood ash in a dry place to prevent it from getting wet or damp. This will help maintain its potency.
2. Test the pH level
Before applying wood ash to your plants, it’s important to test the pH level of your soil. Wood ash can raise the pH level, so if your soil is already alkaline, it may not be suitable for use.
Testing: Use a soil testing kit to determine the pH level of your soil. Aim for a pH level of around 6.5-7 for most plants.
3. Apply the wood ash
Timing: Apply wood ash during the dormant season or in early spring before plants begin to grow. Avoid applying it when plants are actively growing as it may cause nutrient imbalances.
Quantity: Sprinkle a thin layer of wood ash around the base of the plant. Avoid piling up the ash as it can be harmful to the plant.
4. Monitor the plants
After applying the wood ash, monitor your plants for any signs of disease. Wood ash can help prevent diseases caused by fungi and bacteria, such as powdery mildew and blossom end rot.
Observation: Keep an eye out for any improvements or changes in your plants’ health. If you notice any negative effects, such as leaf burn or stunted growth, reduce or stop the application of wood ash.
5. Use it in combination with other remedies
Wood ash can be used in combination with other natural disease remedies to enhance its effectiveness.
Companion plants: Planting disease-resistant companion plants alongside vulnerable plants can help prevent the spread of diseases. Wood ash can be applied to the soil around these companion plants as an additional measure.
Organic sprays: You can also use organic sprays, such as neem oil or garlic spray, in combination with wood ash to further control diseases in plants.
By following these steps, you can make the most of wood ash as a disease remedy and help keep your plants healthy and thriving.
Precautions and Risks of Using Wood Ash
While wood ash can provide numerous benefits as a fertilizer and disease remedy, there are also certain precautions and risks associated with its use. It is important to be aware of these potential drawbacks before incorporating wood ash into your gardening practices.
Contamination
One of the main concerns when using wood ash as a fertilizer is the potential for contamination. Wood ash can contain harmful substances such as heavy metals, which may have been absorbed by the tree during its growth. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that the wood used to produce the ash is free from any contaminants. It is recommended to use wood ash from clean, untreated sources such as hardwood trees or untreated wood products.
pH Imbalance

Wood ash is alkaline in nature and, when applied excessively, can lead to an imbalance in soil pH. This can interfere with the ability of plants to absorb nutrients properly, resulting in nutrient deficiencies or toxicities. It is crucial to test the pH of your soil before applying wood ash and monitor it regularly to ensure it remains within the optimal range for your plants.
Salt Buildup
Wood ash contains potassium carbonate, which can increase the salt levels in the soil. Excessive salt buildup can be harmful to plants, causing dehydration and nutrient imbalances. To prevent salt buildup, it is essential to apply wood ash in moderation and avoid over-fertilizing. Additionally, it is recommended to leach the soil periodically with water to flush out excess salts.
Nutrient Imbalance
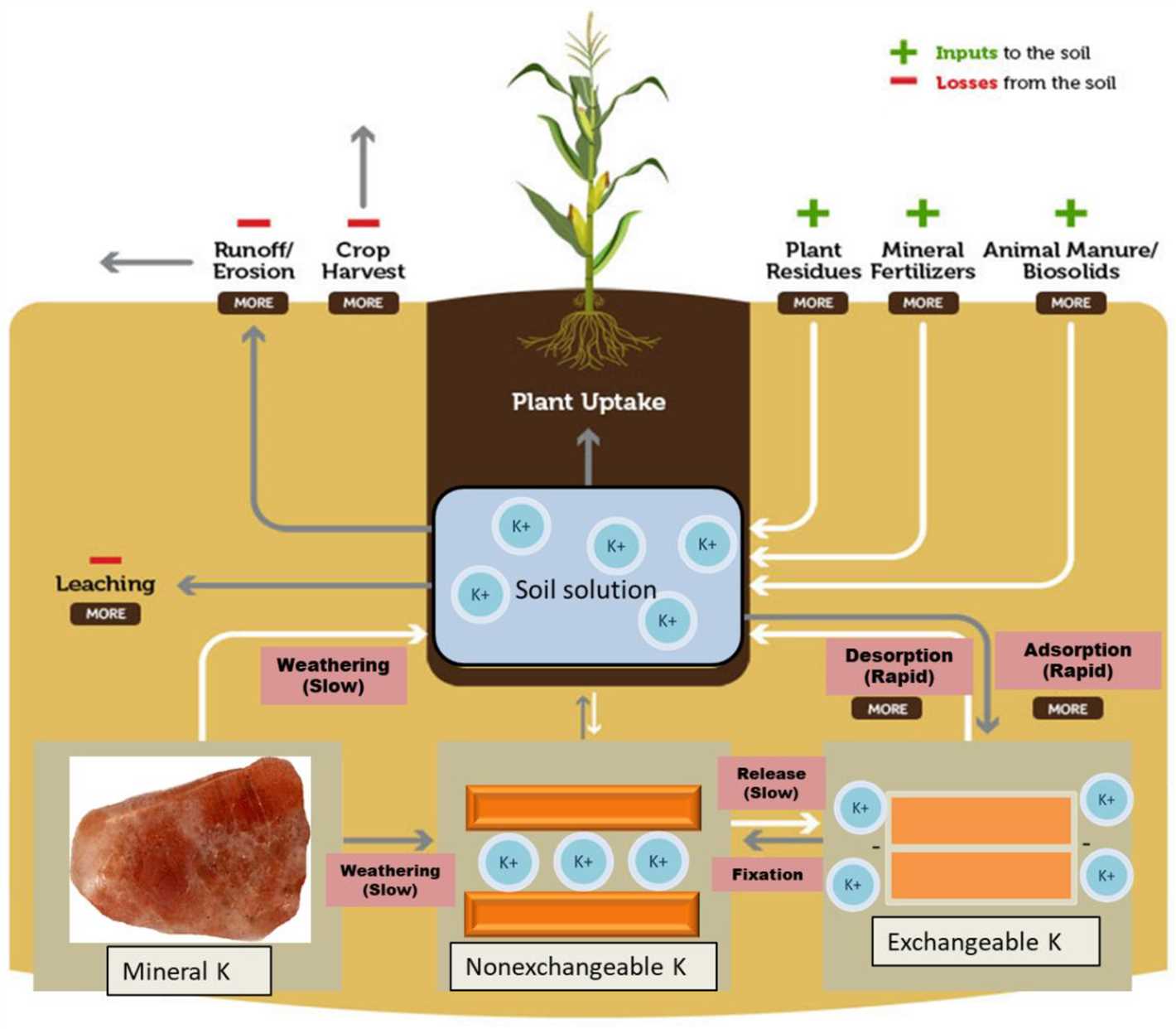
While wood ash can provide essential nutrients such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium to the soil, it should not be used as the sole source of these nutrients. Wood ash lacks important nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, which are vital for plant growth. Therefore, it is important to use wood ash in conjunction with other fertilizers or organic matter to ensure a balanced nutrient supply for your plants.
Environmental Impact
The use of wood ash as a fertilizer may have environmental impacts, especially in sensitive ecosystems. The introduction of excess nutrients into water bodies can lead to eutrophication, which can harm aquatic life. To minimize the environmental impact, it is crucial to apply wood ash responsibly, following recommended application rates and avoiding runoff into waterways.
| Precautions | Risks |
|---|---|
| Ensure wood ash is contaminant-free | Potential contamination with heavy metals |
| Test and monitor soil pH | Possible pH imbalance |
| Apply wood ash in moderation | Increased salt buildup in the soil |
| Use wood ash as a supplement, not a sole nutrient source | Potential nutrient imbalances |
| Apply wood ash responsibly | Possible environmental impact |
In conclusion, while wood ash can be a beneficial fertilizer and disease remedy, it is essential to be cautious and aware of the potential precautions and risks associated with its use. By following recommended guidelines and using wood ash responsibly, you can maximize its benefits while minimizing the potential drawbacks.
“Question-Answer”
What is wood ash?
Wood ash is the powdery residue that remains after burning wood. It is composed primarily of calcium carbonate, which gives it alkaline properties.
What are the benefits of using wood ash as a fertilizer?
Wood ash is a natural source of important nutrients like potassium, calcium, and magnesium. When used as a fertilizer, it can help improve soil pH, promote plant growth, and enhance nutrient availability.
How can wood ash be used to control diseases in plants?
Wood ash has been found to have fungicidal properties, making it effective in controlling certain plant diseases. Its alkaline nature can create an unfavorable environment for fungal growth, helping to prevent or suppress diseases.
Is wood ash suitable for all types of plants?
Wood ash can be used on a variety of plants, but it may not be suitable for all types. Some plants prefer acidic soil, so adding wood ash, which is alkaline, may not be beneficial for them. It is best to test the soil pH and understand the specific needs of the plants before using wood ash as a fertilizer.
How should wood ash be applied as a fertilizer?
Wood ash should be applied sparingly, as excessive use can raise the soil pH to detrimental levels. It is recommended to spread a thin layer of wood ash over the soil surface, avoiding direct contact with plant roots. It can also be mixed with compost or other organic matter before application.
Can wood ash be harmful to plants if used incorrectly?
Yes, if wood ash is used in excessive amounts or applied too frequently, it can raise the soil pH too high, causing nutrient imbalances and inhibiting plant growth. It is important to use wood ash in moderation and consider the specific needs of the plants and soil conditions.
Are there any safety precautions to keep in mind when using wood ash?
Yes, when handling wood ash, it is important to wear gloves and avoid inhaling the dust, as it can be irritating to the skin and respiratory system. It is also advisable to store wood ash in a dry place and keep it away from children and pets.







